23. Thevenin’s theorem
In circuit theory, Thevenin’s theorem for linear electrical networks states that any combination of voltage sources, current sources, and resistors with two terminals is electrically equivalent to a single voltage source V and a single series resistor R. By the equivalent conversion, the voltage, flowing electric current into a load of the connected circuit network can be easily calculated.
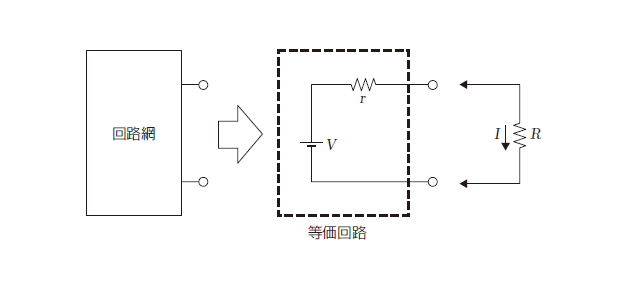
Terminal open voltage of arbitrary 2 points within the circuit
network is assumed as V, the entire voltage source within the
circuit network is assumed as short circuit condition, the
entire current source is assumed as patulous state, and if we
assume the internal resistance seen from the terminal as r, then
the equivalent circuit of this circuit network is a series
circuit of the voltage source of the voltage V and the internal
resistance r. Moreover, the current flows in R, I is given by
the following formula when connected the resistance R in these 2
points.![]()
