28. Transient phenomena
In an electric circuit, the electrical phenomenon during the interval until the stabilization in a separate static state by changes from a certain static state is called the transient phenomena. The following explains about the transient phenomenon of RC series circuit and RL series circuit.
Transient phenomena of RC series circuit
In the series circuit of RC as described below, when the switch
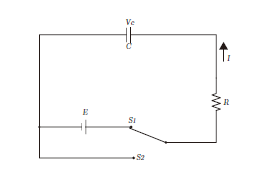
is switching from S2 to S1, the source of direct voltage E[V]
charges electrically the capacitor C[F] through the electrical
resistance R[ω], then the charging current I[A] and the voltage
between the terminals Vc[V] of capacitor C can be expressed as
follows. ![]()
The capacitor is not charged electrically immediately
after switching, and a large charging current flows and the
electric charge is supplied to the capacitor. Vc rises as the
capacitor is charged, the voltage difference between resistance
R becomes lesser, and the charging current decreases. Here, CR
is called time constant
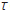 . In the time point of lapsed time
. In the time point of lapsed time
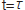 , the Vc rises upto the voltage of
, the Vc rises upto the voltage of
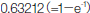 maximum voltage E. This shows the good index of switching
interval when the time constant
maximum voltage E. This shows the good index of switching
interval when the time constant
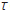 drives the capacitative load. Further, when the switch is
switched to S2, the Vc at the time of discharge current and
electrical discharge is expressed by the following formula. The
voltage between terminals of the capacitor decreases gradually,
and the discharging current flows in the opposite direction of
the charging current.
drives the capacitative load. Further, when the switch is
switched to S2, the Vc at the time of discharge current and
electrical discharge is expressed by the following formula. The
voltage between terminals of the capacitor decreases gradually,
and the discharging current flows in the opposite direction of
the charging current.
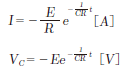
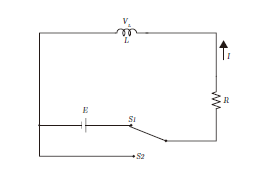
Transient phenomena of RL series circuit
In the series circuit of the following RL, the electric current
I[A] can be expressed by the following formula when the switch
is switched from S2 to S1, and the current flows from source of
direct voltage E V through resistance Rω and inductance L H.
![]()
At first after the switching, the status of the flow of
electric current continues to be less since the inductance L
becomes high impedance for the rapid current change. After that,
the current increases gradually, and afterwards it reaches
I=E/R. Here, the time constant
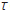 is given by L/R, at the point of lapsed time
is given by L/R, at the point of lapsed time
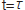 , the current of the value multiplied by
, the current of the value multiplied by
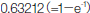 on the final current I=E/R flows. Further, the discharge current
of electromagnetic energy stored in the inductance L when the
switch is switched to S2 is expressed by the following formula.
Electro motive force is caused in the inductance by the
alteration in the magnetic flux according to the current
decrease of inductance, the current keeps flowing in the
direction of the current flowing in the steady state, the
current decreases along with the release of electromagnetic
energy.
on the final current I=E/R flows. Further, the discharge current
of electromagnetic energy stored in the inductance L when the
switch is switched to S2 is expressed by the following formula.
Electro motive force is caused in the inductance by the
alteration in the magnetic flux according to the current
decrease of inductance, the current keeps flowing in the
direction of the current flowing in the steady state, the
current decreases along with the release of electromagnetic
energy.
![]()