35. Boolean algebra
Boolean algebra is a fundamental concept of logical mathematics developed by George Bool in the middle19th century. The combinational circuit can be expressed by the Boolean expression of fundamental Boolean algebra, and the digital circuitry can execute the operation only by “High (High)” and “Low (Low)” voltage by the logical expression of Boolean algebra.
| Theorem | Explanation | |
|---|---|---|
|
Theorem 1 |
|
|
|
Theorem 2 |
|
|
|
Theorem 3 |
|
Idempotent law |
|
Theorem 4 |
|
Idempotent law |
|
Theorem 5 |
|
Complement law |
|
Theorem 6 |
|
Complement law |
|
Theorem 7 |
|
Double negative |
|
Theorem 8 |
|
|
|
Theorem 9 |
|
|
|
Theorem 10 |
|
Commutative rlaw |
|
Theorem 11 |
|
Commutative law |
|
Theorem 12 |
|
Distribution law |
|
Theorem 13 |
|
Associative law |
|
Theorem 14 |
|

|
|
Theorem 15 |
|

|
|
Theorem 16 |
|
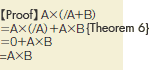
|
|
Theorem 17 |
|

|
|
Theorem 18 |
|

|
|
Theorem 19 |
|
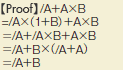
|
|
Theorem 20 |
|
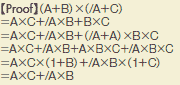
|
|
Theorem 21 |
|
De Morgan’s law |
|
Theorem 22 |
|
De Morgan’s law |
|
Theorem 23 |
|
|
|
Theorem 24 |
|
|
|
Theorem 25 |
|
|
|
Theorem 26 |
|
|
