~Maker Interview~
Where you can read interviews with those in charge of development sites
and product planning talking about their strategies and directions for the future,
focusing on manufacturer hot topics and products they are currently focused on the most.
※Monthly updates of the latest industry trends

Force-guided relays that provide high levels of safety have become indispensable as functional safety standards spread

Leigh Marolf
Do you know what a Force Guided Relay is? A relay is a component that receives an external control signal and turns an electrical circuit on and off. There are various types of relays, but among them, the force-guided relay is for applications that require a particularly high level of safety.
Attention has been on the rise recently for this force-guided relay. Behind this is the spread of functional safety standards. As functional safety standard, "ISO 26262" for in-vehicle equipment is well known, but the target of the functional safety standard is not limited to in-vehicle equipment. IEC 61508, the parent standard of ISO 26262, includes industrial equipment, medical equipment, railways, and home appliances. Force -guided relays comply with functional safety standards, and therefore it is highly likely that force-guided relays will be used in various applications in the future.
TE Connectivity is positioned at the top of the industry in the global market for force-guided relays. According to the company's research, its global market share is upward of 20 to 22%. We asked Mr. Leigh Marolf, who serves as (Senior Product Manager), about the role of forced-guided relays, their main markets, product features, and the direction of future technology and product development.
(Interviewer: Katsumi Yamashita = technology journalist)
To start us off, can you tell us what a forced guided relay is?
What role does it play in electronic equipment?
Marolf Force-guided relays play a role in ensuring that when a failure occurs in the electronic device in which it is installed, the operation is reliably stopped and the device cannot continue to operate. After that, it cannot be turned on again unless the cause of the failure is remedied. In other words, it is a "relay for finding faults".
What are they used for?
Marolf They are used in applications where there is a high risk of loss of life or injury to workers due to malfunction. For example, collaborative robots that work together with humans are one of the typical applications. Forcibly guided relays are used by mounting them on a printed circuit board on which the collaborative robot's control circuit is placed, or by housing them in a safety relay module.
Two contacts that work in pairs
What methods do you use to achieve high levels of safety? I would like to know the principle behind this.
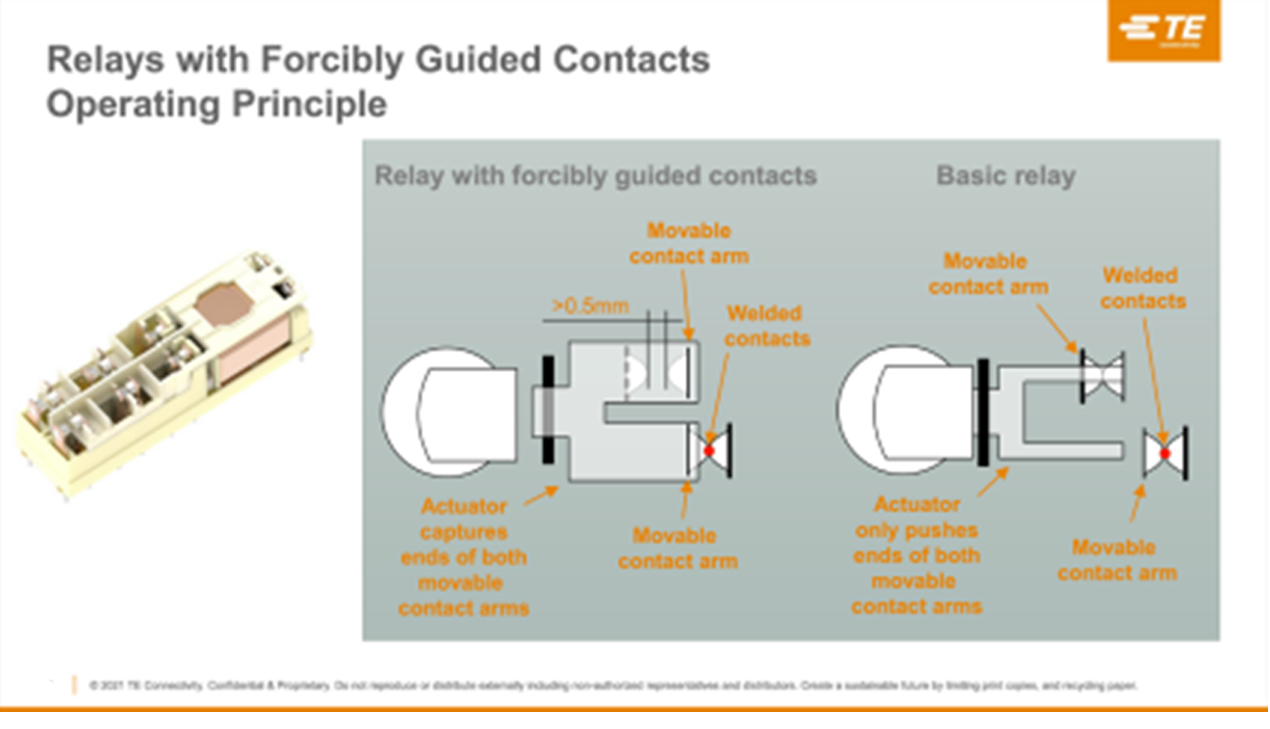
Marolf A relay is a device that connects or disconnects contacts to turn a switch on or off. A typical relay has only one contact. However, as shown in Fig. 2, force-guided relays have two contacts forming a pair. One contact (A contact) is for electrical signal continuity, the same as a general relay. The other contact (B contact) is for failure detection unique to force-guided relays.
These two contacts are interlocked, and when voltage is applied to the electromagnet, the armature (armature) moves and switches the contacts. When no voltage is applied, the A contact is off and the B contact is on. When voltage is applied, the A contact switches on and the B contact switches off.
At this time, if some kind of failure occurs in the application and no voltage is applied, but the A contact is welded and is in the ON state, the two contacts operate together and the B contact turns OFF. In this way, if an application with a force-guided relay fails, you can prevent the electrical signal from conducting and cease operation.
Fig. 3 is a top view of a general relay and a force-guided relay. Comparing both, you can see that a typical relay simply turns the contacts on and off, so even if there are two contacts, if one contact turns on due to welding, etc., the other contact also turns on. There remains a possibility that the general relay may be damaged or lost. However, when one of the force-guided relays is welded on, the other is always off because the two contacts are interlocked by a spring arm. As a result, if a failure occurs, the electric circuit will not be connected, ensuring a high level of safety.
In addition to welding, what kind of failure can be expected?
Marolf Force-guided relays have another failure mode. This addresses the problem when a contact terminal is broken. Figure 4 explains this. If the contact terminal is broken, the part above the broken point may drop, and in the worst case, there is a danger that it will come into contact with the opposite terminal and turn on. Therefore, in the forced-guided relay, an insulating barrier is provided. Even if a contact terminal breaks and falls, it will not touch the opposite terminal, so electricity will not flow through the circuit and the application will not work.
Buildings, railways, and industrial equipment are the three major markets
In what applications are force-guided relays used?
Marolf The three largest markets for force-guided relays are buildings, railroads, and industrial equipment (Fig. 5). In addition, although the market scale is smaller than these, examples of adoption are increasing in medical equipment and emergency power sources.
I would like you to give a specific example and explain what kind of application it is used for.
Marolf Examples of applications in buildings include elevators and escalators (Fig. 6). Applications include door opening / closing, over-speed control, and on / off control of contactors used in places where large currents flow. It is also used in applications such as building entrance / exit gate control, revolving door control, and fire / gas detection.
Examples of applications in railways include opening and closing vehicle doors, switching traffic signals, controlling points on tracks, and controlling railroad crossings (Fig. 7). Both of them are used to safely control various circuits because there is a risk of serious damage in the event of an accident.
In industrial equipment, there are many cases where they are used to protect the safety of workers working in factories. Examples include applications such as metal cutting machines, safety doors, light curtains and conveyor belts (Figure 8). They are equipped with a safety relay module, which contains a force-guided relay. In addition, the number of cases of adoption in automatic guided vehicles (AGVs) used in factories has increased recently.
Examples of applications in medical equipment include magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) inspection equipment and computed tomography (CT) equipment. Specifically, it is used to control the movement of beds on which patients are placed. In the emergency power supply, it is used for switching between the normal power supply and the emergency power supply. In many cases, if an emergency power supply cannot be used due to some kind of failure, it will lead to serious damage or even death. Since failure is absolutely unacceptable, the forced guided relay is used.
Aiming for a 28-30% share
Does TE Connectivity also produce safety relay modules with built-in force-guided relays?
Marolf Currently, we are focusing on the forced guided relay business. In other words, it deals only with the heart of the safety relay module. The reason why the safety relay module has not been commercialized is due to the historical background, and currently our company's mission is to provide the user with the heart of the product. However, from a long-term perspective, we believe it will be necessary to commercialize safety relay modules. In order to make that a reality, we recognize that we need to do some further consideration and look at increasing engineering resources, etc.
Please tell us about TE Connectivity's current share and future share target in the force-guided relay market.
Marolf There are no third-party researched force-guided relay market reports. However, according to our research, we have the top share in the global market, and we estimate that our specific share will reach 20-22%. As for future goals, we aim to achieve a market share of 28-30% in the next five years. To that end, we plan to focus more on markets such as industrial machinery and robots without changing our major policy of providing support (services) close to users (customers) while promoting global development. In particular, these applications have large markets such as China and Japan, so we believe that it will be important to develop markets in both countries.
Where are your design and manufacturing bases located?
Marolf The design base is in Austria, and the manufacturing bases are in Austria, the Czech Republic, and Portugal.
What is the market share of force-guided relays in Japan?
Marolf Our market share is not very high in Japan because there are strong competitors. In Japan, we supply forced guide relays mainly to manufacturers of robots and elevators.
Promoting miniaturization and low power consumption
I would like to know about the product lineup of force-guided relays at TE Connectivity.
Marolf Multiple products are available with different numbers of contacts. There are 2-pole (pole) product “SR2M”, 4-pole (pole) product “SR4M”, 6-pole (pole) product “SR6”, 7-pole (pole) product “SRL7” (Fig. 9). Multiple options are available for coils and contacts, and the number of products exceeds 40. Both products comply with the international standard "IEC 61810-3" for force-guided relays.
What are the advantages when compared to competitors' products?
Marolf The external dimensions and mounting area are small. For example, the width of a 4-pole product is as narrow as 13 mm. Even products with a large number of poles, such as 6-pole and 7-pole products, have been made smaller. The mounting area on the printed circuit board can be reduced by advancing the technology, which is extremely beneficial to the user. Furthermore, the 7-pole product achieves a low profile of 10.8 mm, which is suitable for applications where the mounting height is limited.
Other features include a contact lifespan of over 100,000 times, a high maximum operating temperature of +70°C, and the ability to withstand accelerations up to 20G (G is gravitational acceleration).
Please tell me the relationship between the number of contacts and the number of poles.
Marolf A pole is a point of contact. Therefore, a 2-pole product consists of a pair of A contacts and B contacts. However, the number of A contacts and the number of B contacts of a 4-pole product are not uniquely determined, and can be selected by the user. For example, a configuration with two A contacts and two B contacts (called 2A2B) or a configuration with three A contacts and one B contact (called 3A1B). The user can select the combination of the number of contacts for both 6-pole and 7-pole products. However, the number of A contacts or B contacts cannot be zero. This is because if one of the contacts does not turn off, the function of the forced guided relay cannot be fulfilled.
What kind of products and technologies do you plan to develop in the future? Please tell me as much as possible.
Marolf In the development of new products, we plan to focus on two points. One is miniaturization. This is because many users are demanding further miniaturization. For example, we currently have a 7-pole product. We have a low-profile type, but we are considering expanding this to a 4-pole or 6-pole type. The other is low power consumption. The idea is to further improve efficiency so that the same functions as before can be obtained.
In technology development, we would like to take on the challenge of reducing manufacturing costs. Already today, the manufacturing process for force-guided relays is highly automated. In the future, we would like to reduce costs by further expanding our manufacturing facilities and increasing production efficiency.
Finally, how much impact will COVID-19 and the US-China trade conflict have on TE Connectivity's business?
Marolf It is true that the novel coronavirus has affected our business. However, the impact was not that great. This is because manufacturing processes in the Czech Republic and Portugal are highly automated and require very little manpower. On the other hand, the supply chain had a relatively large impact. We would like to minimize this risk by promoting multi-sourcing of materials and parts in the future.
The trade friction between the US and China is not a big problem because the company has its factories in Europe. However, it is affected by tariffs.
Introduction of TE online store
In addition to the above, we have a wide lineup of TE products!
Allow us to introduce you to TE online store!
Interview with TE manufacturer